Building Scalable Health Tech Solutions: Cloud Computing and Infrastructure Expertise
The healthcare industry stands at a technological inflection point. As data volumes grow exponentially and patient expectations evolve, healthcare organizations are increasingly turning to cloud computing to overcome longstanding infrastructure challenges and create the foundation for next-generation care delivery models.
The Shift Toward Cloud-Based Healthcare Infrastructure
For healthcare organizations, the traditional approach of maintaining on-premises IT infrastructure is becoming increasingly unsustainable. The COVID-19 pandemic served as a powerful catalyst, exposing the limitations of legacy systems and accelerating cloud adoption across the industry.
As Kevin Boyle, CEO of Gearset, notes, "At a time when healthcare providers were strained while providing cutting-edge treatment, it became clear that existing IT infrastructure could be an unnecessary obstacle rather than the key to patient outcomes and data security."1 This realization has prompted a fundamental reassessment of healthcare IT strategy, with cloud computing emerging as the cornerstone of modern healthcare technology infrastructure.
The numbers tell a compelling story: the global market for cloud computing in healthcare is projected to triple in size over the next decade, growing from approximately $70 billion in 2024 to more than $210 billion by 2033.2 This remarkable trajectory reflects healthcare organizations' growing recognition that cloud infrastructure is essential for addressing their most pressing operational and clinical challenges.
Key Advantages of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The shift toward cloud computing offers healthcare organizations numerous advantages over traditional infrastructure approaches:
Enhanced Cost Efficiency and Resource Allocation
Traditional healthcare IT infrastructure often involves significant capital expenditures, ongoing maintenance costs, and the complexity of managing physical servers that may be underutilized much of the time. Cloud computing transforms this model, enabling healthcare organizations to pay only for the computing resources they actually use.
This approach is particularly valuable for healthcare organizations that experience fluctuating demands on their IT resources. A hospital system might need to rapidly scale up its infrastructure during a public health emergency or to support seasonal surges in patient volume. Cloud platforms provide the elasticity to meet these variable demands without the need for large-scale hardware investments.
Accelerated Innovation Through Technological Accessibility
Cloud infrastructure dramatically reduces the barriers to adopting advanced technologies that can transform healthcare delivery. As noted in an industry analysis, "By setting up servers on demand, organizations can implement new technology quickly, whether it's a modernized cloud-based electronic health records (EHR) system, a new predictive modeling application, or a pilot project for chronic care management."2
This capability is particularly valuable in the context of AI and machine learning applications, which often require substantial computing resources. Cloud platforms give healthcare organizations access to the high-performance computing environments needed to train sophisticated algorithms, without requiring them to build and maintain specialized hardware.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
Contrary to early concerns about cloud security, today's leading cloud services providers often deliver security capabilities that exceed what most healthcare organizations could implement independently. Cloud service providers invest heavily in physical security, data encryption, access controls, and threat monitoring—creating environments that meet or exceed regulatory requirements.
For healthcare organizations navigating complex compliance landscapes like HIPAA and GDPR, cloud platforms offer native security features and compliance tools that significantly reduce the burden of maintaining regulatory compliance. This shift allows healthcare IT teams to focus more on strategic initiatives rather than routine security tasks.
Real-World Applications Transforming Healthcare
The theoretical benefits of cloud computing are being realized in practical applications across the healthcare ecosystem:
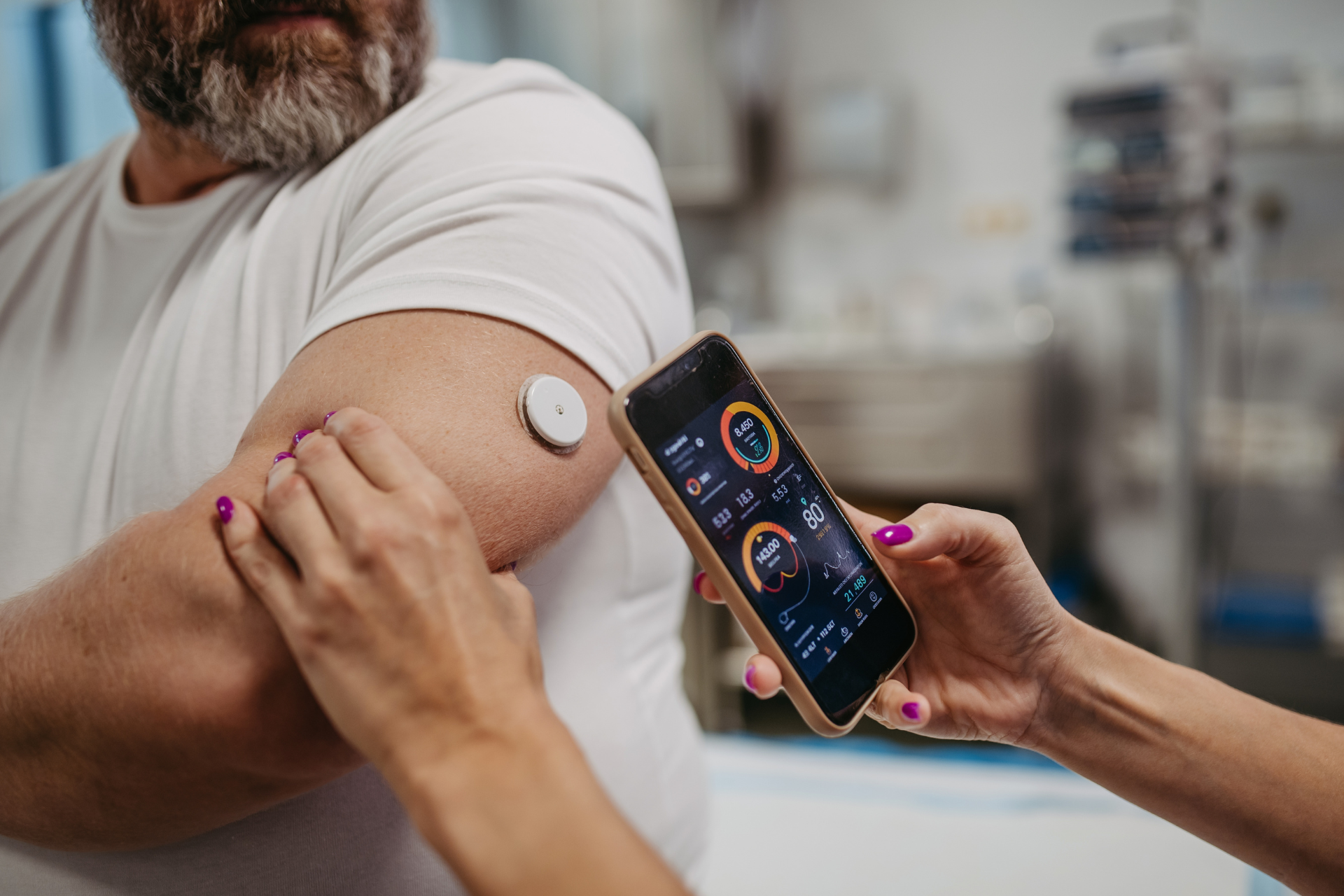
Connected Medical Devices and Remote Monitoring
The growth of networked medical devices—often called the Medical Internet of Things—represents one of the most promising applications of cloud infrastructure in healthcare. By 2029, this software market is projected to reach approximately $134 billion, up from $93 billion in 2025.3
Cloud connectivity enables medical devices to transmit data securely, support remote monitoring, and facilitate real-time interventions. From smart knee implants that track patient rehabilitation to software-enhanced ultrasound machines that leverage AI for image optimization, cloud-connected devices are reshaping how care is delivered and monitored.
For example, Impedimed has developed a cloud-connected device that can detect early signs of lymphedema—a common and debilitating side effect of cancer treatment—allowing for earlier intervention and improved outcomes. The device leverages cloud infrastructure to analyze, store, and transfer patient data, automatically feeding results into electronic health records for seamless integration into clinical workflows.3
Unified Data Environments for Enhanced Analytics
One of cloud computing's most transformative impacts on healthcare has been the creation of unified data environments that break down traditional information silos. When healthcare data is consolidated in cloud platforms, it becomes accessible to authenticated users across the organization, enabling more comprehensive analytics and decision-making.
This capability supports everything from operational efficiency initiatives to advanced clinical research. By creating a single, standardized data repository, healthcare organizations can leverage powerful analytics tools to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and optimize resource allocation with unprecedented precision.
Enabling Telehealth and Virtual Care Models
Cloud infrastructure has been fundamental to the rapid expansion of telehealth and virtual care models. These platforms require robust, scalable infrastructure to support video consultations, remote monitoring, and secure data exchange—capabilities that cloud environments are uniquely positioned to provide.
The flexibility of cloud resources has been particularly valuable as healthcare organizations have worked to rapidly scale their telehealth offerings in response to evolving patient preferences and care delivery models. Organizations that had already invested in cloud infrastructure were able to adapt more quickly to changing requirements, highlighting the strategic value of cloud-based approaches.
Strategic Considerations for Cloud Implementation
While the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare are compelling, successful implementation requires careful planning and strategic decision-making:
Selecting the Right Cloud Model
Healthcare organizations must carefully evaluate different cloud deployment models—public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud—based on their specific requirements for performance, security, compliance, and cost management. Many organizations are finding that hybrid approaches, which combine private cloud environments for sensitive workloads with public cloud resources for other applications, provide an optimal balance.
Developing a Comprehensive Migration Strategy
Moving from legacy systems to cloud infrastructure requires a thoughtful, phased approach that minimizes disruption to critical healthcare operations. Organizations should develop detailed migration roadmaps that prioritize applications based on factors like complexity, interdependencies, and business impact.
Building Cloud Expertise Within Healthcare IT Teams
As healthcare organizations increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure, developing internal expertise becomes essential. IT teams need skills in cloud architecture, security, cost optimization, and integration—capabilities that may require targeted hiring and training initiatives.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
As cloud technologies continue to evolve, healthcare organizations can expect several emerging trends to shape their infrastructure strategies:
- AI Integration: Cloud platforms will increasingly incorporate AI capabilities, enabling healthcare organizations to more easily implement advanced analytics and automation
- Edge Computing: Hybrid architectures that combine cloud resources with edge computing will support applications requiring near real-time processing, such as critical patient monitoring
- Interoperability Enhancements: Cloud-native interoperability solutions will help address the persistent challenge of seamless data exchange across healthcare systems
Building for Success in a Cloud-First Healthcare Environment
For healthcare organizations navigating the transition to cloud infrastructure, several key success factors stand out:
- Executive Sponsorship: Secure strong leadership support for cloud initiatives, recognizing that the transformation extends beyond IT to impact the entire organization
- Break Down Silos: Use cloud migration as an opportunity to address data and operational silos that have historically limited healthcare effectiveness
- Plan for Scalability: Implement cloud architectures that can grow and evolve alongside organizational needs and technological advancements
- Prioritize Security: Maintain unwavering focus on security and compliance throughout the cloud journey, leveraging provider capabilities while maintaining organizational accountability
The shift to cloud computing represents more than a technical evolution—it's a fundamental transformation in how healthcare technology enables better patient care, operational efficiency, and innovation. Organizations that strategically embrace cloud infrastructure position themselves to lead in an increasingly technology-driven healthcare landscape.
To discuss your organization's talent needs in this evolving landscape, contact The Pharma:Health Practice today.
Footnotes
1. "Why Healthcare Is Moving Toward Cloud Computing," Forbes, March 2024.
2. "12 Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare," Oracle NetSuite, February 2025.
3. "Networked devices help head off medical woes and speed recovery," Financial Times, March 2025.